Sending and Receiving Packets
1. Introduction
Sending and receiving one byte of data is simple. But what if you want to send and receive multiple bytes of data? Now, you need to think of a way to structure the data so that the receiver can determine the first byte when receiving bytes continuously. Long bytes of data are prone to errors. Now, you need to think of error detection. Let’s start packetizing data.
A simple packet contains sunchronization bytes, data and error detection bytes. The simple synchronization method is using start bytes. Start bytes have a value which also can be present in data. The error detection bytes play important role to detect any misalignment and errors. There are techniques to calculate error detection bytes. The simple technique is checksum and a better technique is cyclic redundancy check (CRC).
2. Understanding Checksum
It is really easy to calculate checksum of data packet. Checksum is calculated using two method.
2.1. Addition based Checksum
Checksum is calculated by adding each bytes of data. The addtion can overflowe if size of checksum is small. Consider size of checksum is one byte. Let’s write test code to calculate checksum of bytes using addition.
1#include <stdio.h>
2#include <stdint.h>
3
4uint8_t getAddBasedChecksum(uint8_t *data, size_t len)
5{
6 uint8_t checksum = 0;
7 size_t i;
8
9 for (i = 0; i < len; ++i)
10 {
11 checksum += data[i];
12 }
13
14 return checksum;
15}
16
17int main()
18{
19 uint8_t data[] = {11, 22, 33, 44, 55, 66, 79, 89, 99, 100};
20
21 uint32_t checksum = getAddBasedChecksum(data, sizeof(data));
22 printf("checksum: %02X\n", checksum);
23
24 return 0;
25}
Compile and run this test code.
2.2. XOR based Checksum
Let’s talk about binary addition and XOR.
Addition |
XOR |
|---|---|
0 + 0 = 0 |
0 XOR 0 = 0 |
0 + 1 = 1 |
0 XOR 1 = 1 |
1 + 0 = 1 |
1 XOR 0 = 1 |
1 + 1 = 0 (carry 1) |
1 XOR 1 = 0 |
Binary Addition and XOR are same for first three. But for two 1’s, Addition takes carry but XOR neglects it. Let’s write test code for XOR based checksum calculation.
1#include <stdio.h>
2#include <stdint.h>
3
4uint8_t getXORBasedChecksum(uint8_t *data, size_t len)
5{
6 uint8_t checksum = 0;
7 size_t i;
8
9 for (i = 0; i < len; ++i)
10 {
11 checksum ^= data[i];
12 }
13
14 return checksum;
15}
16
17int main()
18{
19 uint8_t data[] = {11, 22, 33, 44, 55, 66, 79, 89, 99, 100};
20
21 uint32_t checksum = getXORBasedChecksum(data, sizeof(data));
22 printf("checksum: %02X\n", checksum);
23
24 return 0;
25}
Compile and run this code.
3. Need of CRC
Checksum is simple and fast but there is high chance of collision. Suppose two bytes having value 3 and 4. The sum is 7. Also suppose two bytes having vallue 5 and 2. The sum is 7 too. It is failure of checksum.
We have already discussed about CRC in previous tutorial. The CRC template class was general but it is bettr to have specific CRC class that has to be used for performance. Let’s write a simple SMBus CRC-8 class.
4. Implementing SMBus CRC-8
Let’s create header and souce file.
1/**
2 ******************************************************************************
3 * @file crc8.hpp
4 * @brief Header file 8-bit SMBus CRC calculation
5 * @author Robotics Team, IOE Pulchowk Campus
6 ******************************************************************************
7 */
8
9#ifndef CRC8_HPP
10#define CRC8_HPP
11
12#include <stdint.h>
13
14#define CRC8_SMBUS_POLYNOMIAL 0x07 /**< CRC-8 polynomial for SMBus. */
15
16/**
17 * @brief Class for CRC-8 checksum calculation.
18 */
19class CRC8
20{
21public:
22 /**
23 * @brief Calculate CRC-8 checksum for uint8_t type data.
24 * @param buf Pointer to the data buffer.
25 * @param len Length of the data buffer.
26 * @return CRC-8 checksum value.
27 */
28 static uint8_t get_hash(const uint8_t *data, const uint16_t len);
29
30 /**
31 * @brief Print the CRC hash table.
32 */
33 static void print_table();
34
35 static uint8_t get_polynomial() { return polynomial_; } /**< Get the CRC polynomial. */
36 static uint8_t get_check() { return check_; } /**< Get the CRC check value. */
37 static const uint8_t *get_table() { return table_; } /**< Get the CRC hash table. */
38
39 static CRC8 Instance; /**< Singleton instance of CRC8 class. */
40
41private:
42 static uint8_t polynomial_; /** CRC polynomial **/
43 static uint8_t check_; /**< CRC check value. */
44 static uint8_t table_[256]; /**< CRC hash table. */
45
46 /**
47 * @brief Private constructor for CRC8 class.
48 */
49 CRC8();
50
51 /**
52 * @brief Initialize the CRC hash table.
53 */
54 static void initialize_table();
55};
56
57#endif // CRC_HPP
The constructor of CRC8 class is private so no multiple instances will be created by user except one we created as static member. Such type of class is called singletone class.
1/**
2 * *********************************************************************************************
3 * @file crc8.cpp
4 * @brief Implementation file for the 8-bit SMBus CRC class
5 * @author Robotics Team, IOE Pulchowk Campus
6 * @date 2024
7 *
8 * For more information on CRC calculation in C, \
9 * see \link https://barrgroup.com/embedded-systems/how-to/crc-calculation-c-code \endlink.
10 ***********************************************************************************************
11 */
12
13#include <stdio.h>
14#include "crc8.hpp"
15
16CRC8 CRC8::Instance;
17uint8_t CRC8::polynomial_;
18uint8_t CRC8::check_;
19uint8_t CRC8::table_[256];
20
21CRC8::CRC8()
22{
23 polynomial_ = CRC8_SMBUS_POLYNOMIAL;
24 initialize_table();
25
26 uint8_t data[] = {'1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9'};
27 check_ = get_hash(data, sizeof(data));
28}
29
30void CRC8::initialize_table()
31{
32 uint8_t remainder;
33 int dividend;
34 int bit;
35
36 for (dividend = 0; dividend < 256; ++dividend)
37 {
38 remainder = dividend;
39
40 for (bit = 8; bit > 0; --bit)
41 {
42 if (remainder & 0x80)
43 {
44 remainder = (remainder << 1) ^ polynomial_;
45 }
46 else
47 {
48 remainder = (remainder << 1);
49 }
50 }
51 table_[(uint8_t)dividend] = remainder;
52 }
53}
54
55uint8_t CRC8::get_hash(const uint8_t *data, uint16_t len)
56{
57 uint8_t remainder = 0;
58 uint8_t dividend;
59 int i;
60
61 for (i = 0; i < len; ++i)
62 {
63 dividend = data[i] ^ remainder;
64 remainder = table_[dividend];
65 }
66
67 return remainder;
68}
69
70void CRC8::print_table()
71{
72 for (int i = 0; i < 256; ++i)
73 {
74 printf("0x%02X, ", table_[i]);
75 if ((i + 1) % 8 == 0)
76 {
77 printf("\n");
78 }
79 }
80 printf("\n");
81}
To ensure the CRC8 compatibility with other CRC8, the loockup table and check value are compared. Now write the test code.
1#include <iostream>
2#include "crc8.hpp"
3
4int main()
5{
6 CRC8::print_table();
7 uint8_t data[] = {'1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9'};
8 std::cout.setf(std::ios::hex, std::ios::basefield);
9 std::cout << "CRC-8 hash: " << (int)CRC8::Instance.get_hash(data, sizeof(data)) << std::endl;
10 return 0;
11}
Compile and run this code.
g++ crc8.cpp crc8_test.cpp -o crc8_test
./crc8_test
0x00, 0x07, 0x0E, 0x09, 0x1C, 0x1B, 0x12, 0x15,
0x38, 0x3F, 0x36, 0x31, 0x24, 0x23, 0x2A, 0x2D,
0x70, 0x77, 0x7E, 0x79, 0x6C, 0x6B, 0x62, 0x65,
0x48, 0x4F, 0x46, 0x41, 0x54, 0x53, 0x5A, 0x5D,
0xE0, 0xE7, 0xEE, 0xE9, 0xFC, 0xFB, 0xF2, 0xF5,
0xD8, 0xDF, 0xD6, 0xD1, 0xC4, 0xC3, 0xCA, 0xCD,
0x90, 0x97, 0x9E, 0x99, 0x8C, 0x8B, 0x82, 0x85,
0xA8, 0xAF, 0xA6, 0xA1, 0xB4, 0xB3, 0xBA, 0xBD,
0xC7, 0xC0, 0xC9, 0xCE, 0xDB, 0xDC, 0xD5, 0xD2,
0xFF, 0xF8, 0xF1, 0xF6, 0xE3, 0xE4, 0xED, 0xEA,
0xB7, 0xB0, 0xB9, 0xBE, 0xAB, 0xAC, 0xA5, 0xA2,
0x8F, 0x88, 0x81, 0x86, 0x93, 0x94, 0x9D, 0x9A,
0x27, 0x20, 0x29, 0x2E, 0x3B, 0x3C, 0x35, 0x32,
0x1F, 0x18, 0x11, 0x16, 0x03, 0x04, 0x0D, 0x0A,
0x57, 0x50, 0x59, 0x5E, 0x4B, 0x4C, 0x45, 0x42,
0x6F, 0x68, 0x61, 0x66, 0x73, 0x74, 0x7D, 0x7A,
0x89, 0x8E, 0x87, 0x80, 0x95, 0x92, 0x9B, 0x9C,
0xB1, 0xB6, 0xBF, 0xB8, 0xAD, 0xAA, 0xA3, 0xA4,
0xF9, 0xFE, 0xF7, 0xF0, 0xE5, 0xE2, 0xEB, 0xEC,
0xC1, 0xC6, 0xCF, 0xC8, 0xDD, 0xDA, 0xD3, 0xD4,
0x69, 0x6E, 0x67, 0x60, 0x75, 0x72, 0x7B, 0x7C,
0x51, 0x56, 0x5F, 0x58, 0x4D, 0x4A, 0x43, 0x44,
0x19, 0x1E, 0x17, 0x10, 0x05, 0x02, 0x0B, 0x0C,
0x21, 0x26, 0x2F, 0x28, 0x3D, 0x3A, 0x33, 0x34,
0x4E, 0x49, 0x40, 0x47, 0x52, 0x55, 0x5C, 0x5B,
0x76, 0x71, 0x78, 0x7F, 0x6A, 0x6D, 0x64, 0x63,
0x3E, 0x39, 0x30, 0x37, 0x22, 0x25, 0x2C, 0x2B,
0x06, 0x01, 0x08, 0x0F, 0x1A, 0x1D, 0x14, 0x13,
0xAE, 0xA9, 0xA0, 0xA7, 0xB2, 0xB5, 0xBC, 0xBB,
0x96, 0x91, 0x98, 0x9F, 0x8A, 0x8D, 0x84, 0x83,
0xDE, 0xD9, 0xD0, 0xD7, 0xC2, 0xC5, 0xCC, 0xCB,
0xE6, 0xE1, 0xE8, 0xEF, 0xFA, 0xFD, 0xF4, 0xF3,
CRC-8 hash: f4
5. Sending Packets through UART using Arduino
Let’s suppose you want to send packets that contains joystick data twist(vx, vy, w). To do so, select one start byte 0xA5, then three bytes for vx, vy and w, and one byte for CRC.
Create a
new sketchinArduino IDE. Save it assending_packets.Open
terminalin theArduino IDEusingctrl+`. Create filescrc8.hppandcrc8.cpp.touch crc8.hpp touch crc8.cpp
Copy the contents of
crc8.hppandcrc8.cppfrom above section 4.Now copy and paste these contensts in
sending_packets.ino.sending_packets.ino1#include "crc8.hpp" 2 3struct Twist { 4 float vx; 5 float vy; 6 float w; 7}; 8 9const uint8_t START_BYTE = 0xA5; 10const uint8_t LED_PIN = 13; 11 12Twist twist; 13uint8_t sending_packet[sizeof(Twist) + 2]; 14uint32_t last_sent_tick = 0; 15uint32_t last_blinked_tick = 0; 16 17void blink_led() 18{ 19 if (millis() - last_blinked_tick < 100) 20 return; 21 22 digitalWrite(LED_PIN, !digitalRead(LED_PIN)); 23 last_blinked_tick = millis(); 24} 25 26void setup() { 27 Serial.begin(115200); 28 pinMode(LED_PIN, OUTPUT); 29 delay(100); 30} 31 32void loop() { 33 uint32_t now = millis(); 34 if (now - last_sent_tick < 10) 35 return; 36 37 twist.vx = 0.5f; 38 twist.vy = 0.5f; 39 twist.w = 0.0f; 40 41 sending_packet[0] = START_BYTE; 42 memcpy(sending_packet+1, &twist, sizeof(twist)); 43 sending_packet[sizeof(sending_packet) -1] = CRC8::get_hash((uint8_t*)(&twist), sizeof(twist)); 44 45 Serial.write(sending_packet, sizeof(sending_packet)); 46 blink_led(); 47 48 last_sent_tick = now; 49}
Compile and upload the code to your
Arduino.
6. Receiving Packets through UART using Arduino
Now you have to receive packets and parse them. The format used for sending packets should be same while parsing.
Create a
new sketchinArduino IDE. Save it asreceiving_packets.Open
terminalin theArduino IDEusingctrl+`. Create filescrc8.hppandcrc8.cpp.touch crc8.hpp touch crc8.cpp
Copy the contents of
crc8.hppandcrc8.cppfrom above section 4.Now copy and paste these contensts in
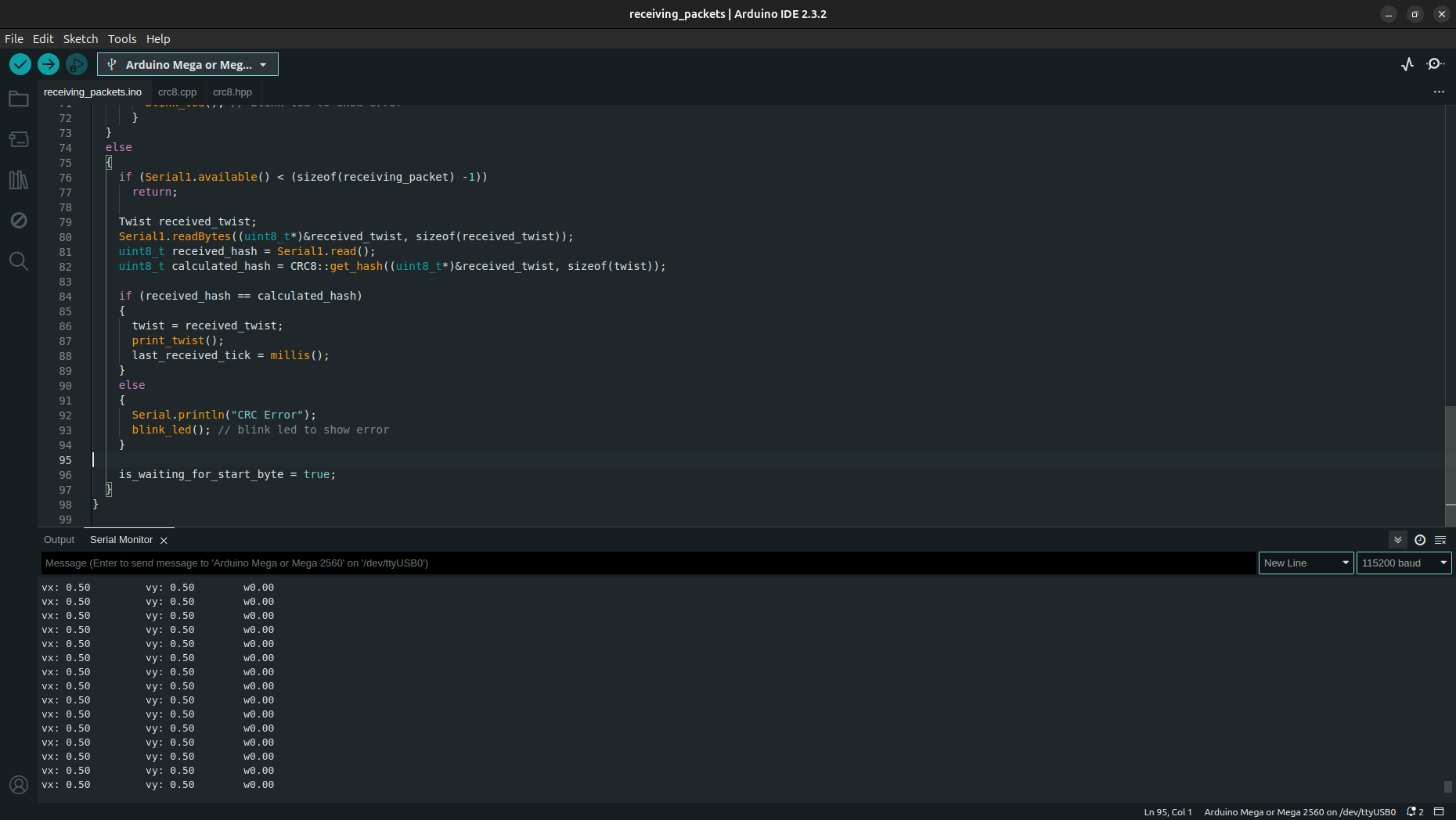
receiving_packets.ino.receiving_packets.ino1#include "crc8.hpp" 2 3struct Twist { 4 float vx; 5 float vy; 6 float w; 7}; 8 9const uint8_t START_BYTE = 0xA5; 10const uint8_t LED_PIN = 13; 11 12Twist twist = {0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f}; 13uint8_t receiving_packet[sizeof(Twist) + 2]; 14 15uint32_t last_received_tick = 0; 16uint32_t last_blinked_tick = 0; 17uint32_t last_printed_tick = 0; 18 19bool is_waiting_for_start_byte = true; 20 21char print_buffer[100]; 22 23void blink_led(); 24void print_twist(); 25 26void blink_led() 27{ 28 if (millis() - last_blinked_tick < 100) 29 return; 30 31 digitalWrite(LED_PIN, !digitalRead(LED_PIN)); 32 last_blinked_tick = millis(); 33} 34 35void print_twist() 36{ 37 if (millis() - last_printed_tick < 100) 38 return; 39 40 Serial.print("vx: "); 41 Serial.print(twist.vx); 42 Serial.print("\t vy: "); 43 Serial.print(twist.vy); 44 Serial.print("\t w"); 45 Serial.println(twist.w); 46 47 last_printed_tick = millis(); 48} 49 50void setup() { 51 Serial.begin(115200); 52 Serial1.begin(115200); 53 pinMode(LED_PIN, OUTPUT); 54 delay(100); 55} 56 57void loop() { 58 if (is_waiting_for_start_byte) 59 { 60 if (Serial1.available() < 1) 61 return; 62 63 uint8_t received_start_byte = Serial1.read(); 64 if (received_start_byte == START_BYTE) 65 { 66 is_waiting_for_start_byte = false; 67 } 68 else 69 { 70 Serial.println("Start Byte Error!"); 71 blink_led(); // blink led to show error 72 } 73 } 74 else 75 { 76 if (Serial1.available() < (sizeof(receiving_packet) -1)) 77 return; 78 79 Twist received_twist; 80 Serial1.readBytes((uint8_t*)&received_twist, sizeof(received_twist)); 81 uint8_t received_hash = Serial1.read(); 82 uint8_t calculated_hash = CRC8::get_hash((uint8_t*)&received_twist, sizeof(twist)); 83 84 if (received_hash == calculated_hash) 85 { 86 twist = received_twist; 87 print_twist(); 88 last_received_tick = millis(); 89 } 90 else 91 { 92 Serial.println("CRC Error"); 93 blink_led(); // blink led to show error 94 } 95 96 is_waiting_for_start_byte = true; 97 } 98}
This receiving code is written for
Arduino Mega. You may want to modify it for other boards. It is better to use microcontroller having atleast two UARTs likeArduino Megahas three UARTs.Compile and upload the code to your
Arduino.Connect the
TX pinofSenderandRX pinofReceiver. CommonGNDof both.Open
Serial Monitorin theArduino IDE. Set boudrate to115200or that in your code. You will see the parsed data.
Note
It is better to include start byte in the CRC calculation. So if data are misaligned, the CRC will not match. The receiver will discard the packet and wait for next packet.
For example, CRC of one byte 0x12 is same as CRC of two bytes 0x00 and 0x12 because of adding 0 at the left of a number does not change its value i.e. 0x12 is equal to 0x0012. But if you include start byte, the CRC will be different.
Note
The more standard way to check error at receiver side is to calculate CRC of data including CRC sent from transmitter. If the accumulated CRC is 0, then the data is correct. If not, then there is error in the data.
7. Sending Packets through UART using STM32
Create and generate new STM32 project using STM32CubeMX.
Project Name:sending_packetsMicrocontroller:STM32F103C8or any other STM32 microcontrollerToolchain/IDE:MakefileorCMake
Go to
Connectivityand select anyUSARTwith modeAsynchronous. UnderDMA settings, enableDMAforTransmit. Follow the UART with DMA tutorial to setup more details.Also assign an
LEDpin forGPIO_Output.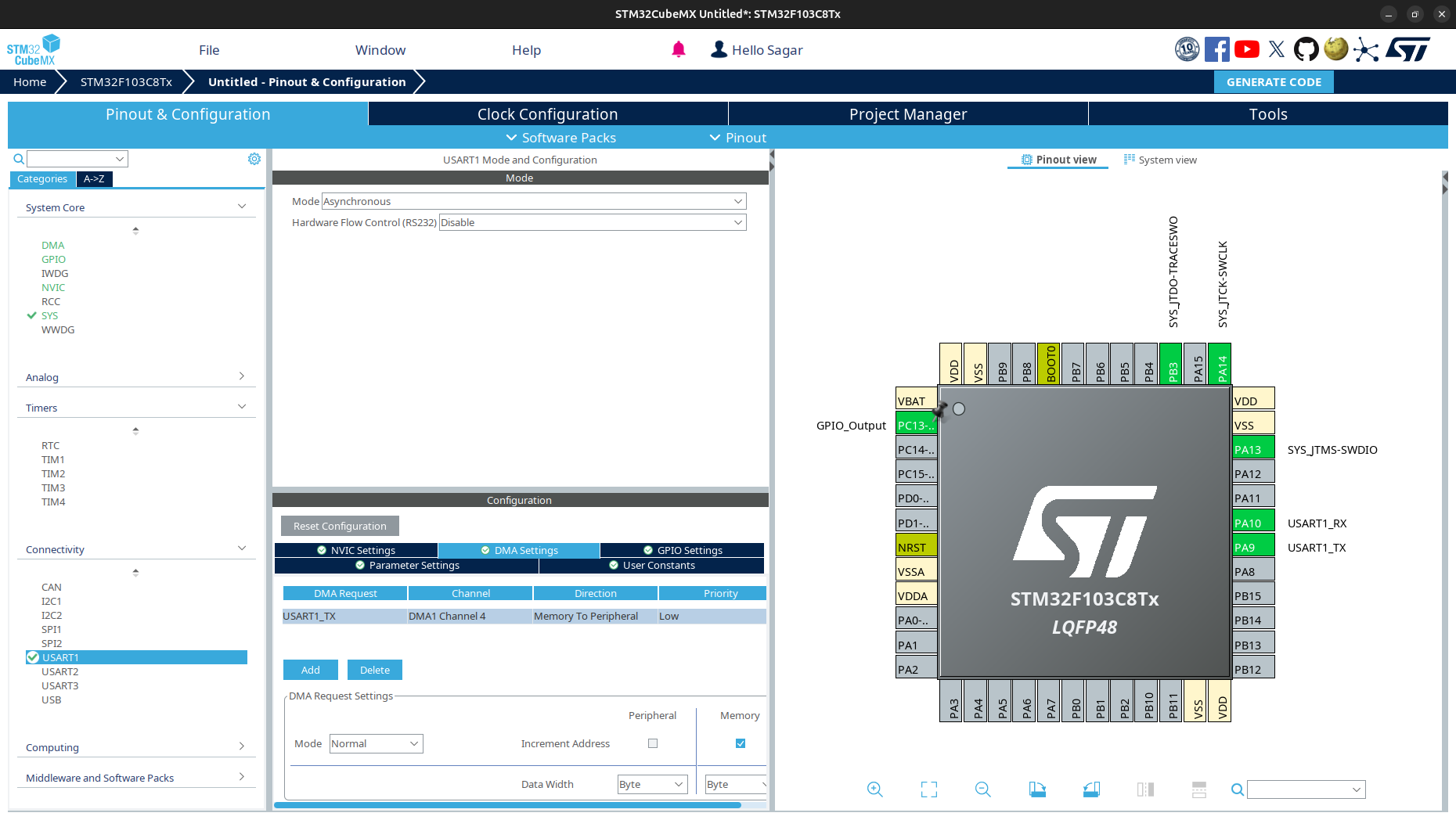
Follow C++ setup tutorial and setup up to compile
C++souce codes. In the C++ setup tutorial, you have already createdapp.handapp.cpp, and blinked the LED. Reach to that point.Create a new file
crc8.hppandcrc8.cppinCore > IncandCore > Srcrespectively. Copy the contents ofcrc8.hppandcrc8.cppfrom above section 4.Update
app.handapp.cppp.app.h1#ifndef __APP_H 2#define __APP_H 3 4#ifdef __cplusplus 5extern "C" { 6#endif 7 8void setup(); 9 10void loop(); 11 12void blink_led(); 13 14#ifdef __cplusplus 15} 16#endif 17 18#endif // __APP_H
app.cpp1#include <memory.h> 2 3#include "stm32f1xx_hal.h" 4#include "usart.h" 5#include "crc8.hpp" 6#include "app.h" 7 8#define START_BYTE 0xA5 9 10struct Twist 11{ 12 float vx; 13 float vy; 14 float w; 15}; 16 17Twist twist = {0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f}; 18uint8_t transmitting_bytes[sizeof(Twist) + 2]; 19 20uint32_t last_tranmsit_tick = 0; 21uint32_t last_led_blink_tick = 0; 22 23void setup() 24{ 25} 26 27void loop() 28{ 29 if (HAL_GetTick() - last_tranmsit_tick < 10) 30 return; 31 32 twist.vx = 0.5f; 33 twist.vy = 0.5f; 34 twist.w = 0.0f; 35 36 transmitting_bytes[0] = START_BYTE; 37 memcpy(transmitting_bytes + 1, &twist, sizeof(twist)); 38 transmitting_bytes[sizeof(transmitting_bytes) - 1] = CRC8::get_hash((uint8_t *)&twist, sizeof(twist)); 39 40 HAL_UART_Transmit_DMA(&huart1, (uint8_t *)transmitting_bytes, sizeof(transmitting_bytes)); 41 42 last_tranmsit_tick = HAL_GetTick(); 43} 44 45void blink_led() 46{ 47 if (HAL_GetTick() - last_led_blink_tick > 100) 48 { 49 HAL_GPIO_TogglePin(GPIOC, GPIO_PIN_13); 50 last_led_blink_tick = HAL_GetTick(); 51 } 52} 53 54// Make sure you have enabled the UART interrupt in the CubeMX 55void HAL_UART_TxCpltCallback(UART_HandleTypeDef *huart) 56{ 57 if (huart->Instance == huart1.Instance) 58 { 59 blink_led(); 60 } 61}
Add souces to
MakefileorCMakeLists.txt.Build and upload the code to your
STM32.
8. Receiving Packets through UART using STM32
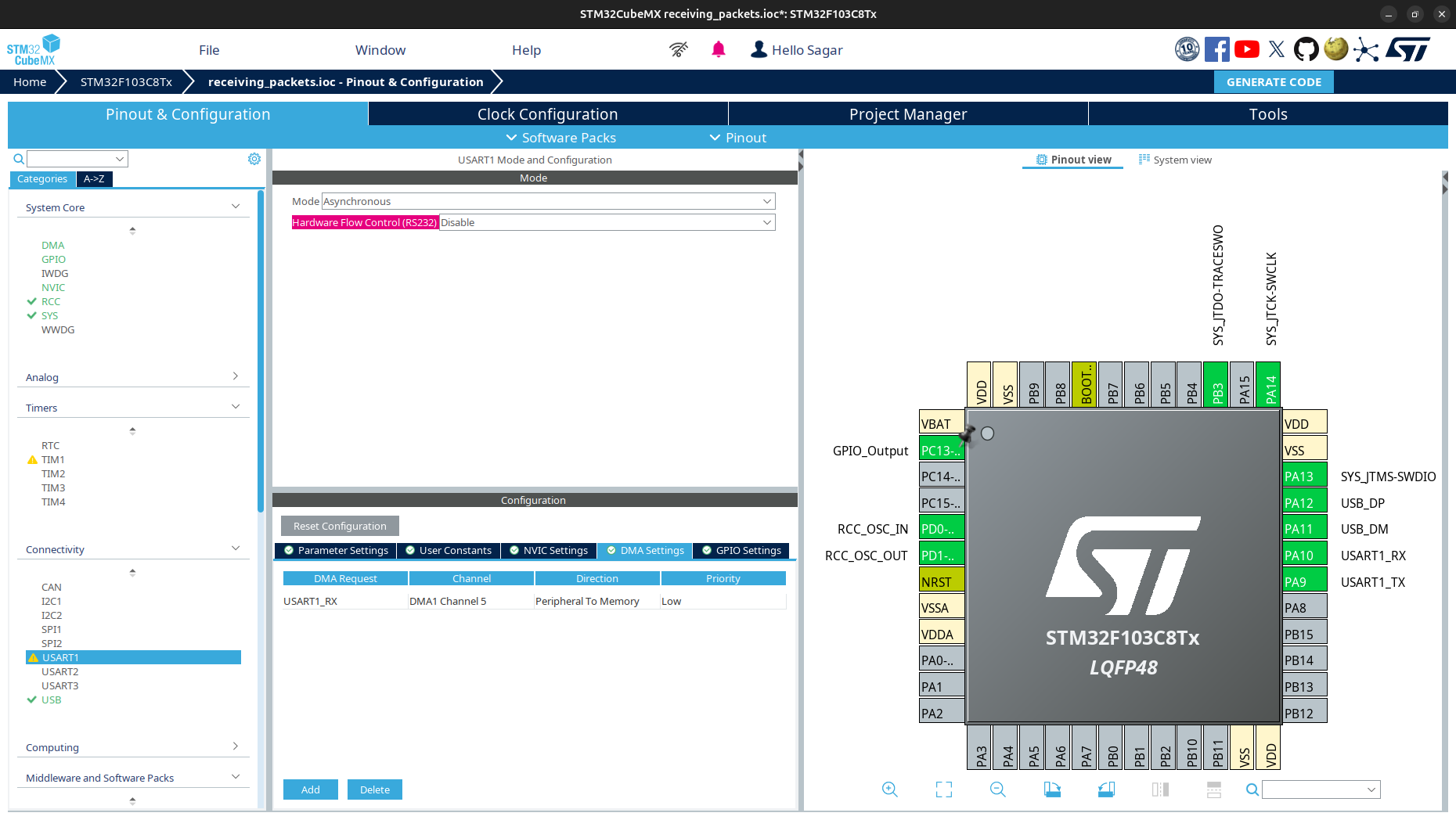
Create and generate new STM32 project using STM32CubeMX.
Project Name:receiving_packetsMicrocontroller:STM32F103C8or any other STM32 microcontrollerToolchain/IDE:MakefileorCMake
Go to
Connectivityand select anyUSARTwith modeAsynchronous. UnderDMA settings, enableDMAforReceive. Follow the UART with DMA tutorial to setup more details.Assign assign an
LEDpin forGPIO_Output.If you want to print overUSB, enableUSBandVirtual COM Port. See USB tutorial.
Follow C++ setup tutorial and setup up to compile
C++souce codes. In the C++ setup tutorial, you have already createdapp.handapp.cpp, and blinked the LED. Reach to that point.Create a new file
crc8.hppandcrc8.cppinCore > IncandCore > Srcrespectively. Copy the contents ofcrc8.hppandcrc8.cppfrom above section 4.Add
printf_config.cinCore > Src. Copy the contents below.printf_config.c1#include "stm32f1xx_hal.h" 2 3#define USE_USB_CDC 4#ifdef USE_USB_CDC 5 6#include "usbd_cdc_if.h" 7 8int _write(int file, char *data, int len) 9{ 10 CDC_Transmit_FS((uint8_t*)data, (uint16_t)len); 11 return len; 12} 13 14#else 15 16int _write(int file, char *data, int len) 17{ 18 for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i) 19 { 20 ITM_SendChar(data[i]); 21 } 22 return len; 23} 24 25#endif
Change definition to use
ITM.Update
app.handapp.cpp.app.h1#ifndef __APP_H 2#define __APP_H 3 4#ifdef __cplusplus 5extern "C" { 6#endif 7 8void setup(); 9 10void loop(); 11 12void blink_led(); 13 14void print_twist(); 15 16#ifdef __cplusplus 17} 18#endif 19 20#endif // __APP_H
app.cpp1#include <memory.h> 2#include <stdio.h> 3 4#include "stm32f1xx_hal.h" 5#include "usart.h" 6#include "crc8.hpp" 7#include "app.h" 8 9#define START_BYTE 0xA5 10 11struct Twist 12{ 13 float vx; 14 float vy; 15 float w; 16}; 17 18Twist twist = {0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f}; 19uint8_t receiving_bytes[sizeof(Twist) + 2]; 20bool is_waiting_for_start_byte = true; 21uint16_t rx_seq = 0; 22uint16_t used_rx_seq = 0; 23 24uint32_t last_receive_tick = 0; 25uint32_t last_led_blink_tick = 0; 26uint32_t last_print_tick = 0; 27 28 29void setup() 30{ 31 HAL_UART_Receive_DMA(&huart1, (uint8_t *)receiving_bytes, 1); 32 is_waiting_for_start_byte = true; 33} 34 35void loop() 36{ 37 if (HAL_GetTick() - last_tranmsit_tick < 10) 38 return; 39 40 if (rx_seq != used_rx_seq) 41 { 42 print_twist(); 43 used_rx_seq = rx_seq; 44 } 45 46 if (huart1.gstate != HAL_UART_STATE_BUSY_TX) 47 { 48 HAL_UART_Receive_DMA(&huart1, (uint8_t *)receiving_bytes, 1); 49 is_waiting_for_start_byte = true; 50 blink_led(); // blink led to show error 51 } 52 53 last_tranmsit_tick = HAL_GetTick(); 54} 55 56void blink_led() 57{ 58 if (HAL_GetTick() - last_led_blink_tick > 100) 59 { 60 HAL_GPIO_TogglePin(GPIOC, GPIO_PIN_13); 61 last_led_blink_tick = HAL_GetTick(); 62 } 63} 64 65void print_twist() 66{ 67 if (HAL_GetTick() - last_print_tick > 100) 68 { 69 printf("vx: %f, vy: %f, w: %f\n", twist.vx, twist.vy, twist.w); 70 last_print_tick = HAL_GetTick(); 71 } 72} 73 74void HAL_UART_RxCpltCallback(UART_HandleTypeDef *huart) 75{ 76 __HAL_UART_FLUSH_DRREGISTER(huart); 77 78 if (huart->Instance == huart1.Instance) 79 { 80 if (is_waiting_for_start_byte) 81 { 82 // verify start byte 83 if (receiving_bytes[0] == START_BYTE) 84 { 85 HAL_UART_Receive_DMA(&huart1, (uint8_t *)receiving_bytes + 1, sizeof(Twist) + 1); 86 is_waiting_for_start_byte = false; 87 } 88 else 89 { 90 HAL_UART_Receive_DMA(&huart1, (uint8_t *)receiving_bytes, 1); 91 blink_led(); // blink led to show error 92 } 93 } 94 else 95 { 96 // verify hash 97 if (receiving_bytes[sizeof(receiving_bytes) - 1] == CRC8::get_hash(receiving_bytes + 1, sizeof(Twist))) 98 { 99 memcpy(&twist, receiving_bytes + 1, sizeof(Twist)); 100 rx_seq++; 101 } 102 else 103 { 104 blink_led(); // blink led to show error 105 } 106 107 is_waiting_for_start_byte = true; 108 last_receive_tick = HAL_GetTick(); 109 } 110 } 111} 112 113void HAL_UART_ErrorCallback(UART_HandleTypeDef *huart) 114{ 115 __HAL_UART_FLUSH_DRREGISTER(huart); 116 117 if (huart->Instance == huart1.Instance) 118 { 119 HAL_UART_Receive_DMA(&huart1, (uint8_t *)receiving_bytes, 1); 120 is_waiting_for_start_byte = true; 121 blink_led(); // blink led to show error 122 } 123}
Add souces to
MakefileorCMakeLists.txt.Build and upload the code to your
STM32.
Connect the TX pin of Sender and RX pin of Receiver. Common GND of both. Observe the data on USB or ITM using Serial Monitor or Terminal or STM32CubeProgrammer SWV.