USB CDC
1. Introduction
USB CDC (Communication Device Class) is a class of USB devices that are used to transmit data between a computer and a USB device. The USB CDC class is used to emulate a serial port over USB. This allows the USB device to be used as a virtual COM port. The USB CDC class is commonly used in microcontroller projects to provide a simple and easy way to communicate with a computer.
2. CubeMX Configuration
Open STM32CubeMX, create a new project and set up basic configuration. Follow the generate_basic_code with:
microcontroller:
stm32f407vgt6or board:STM32F407VG-DISC1project name:
usb_exampleToolchain/IDE:
Makefile
Move to STM32CubeMX
Pinout and Congiguration. FromCategories, selectConnectivity > USB_OTG_FS. ChangemodetoDevice_Onlymode.
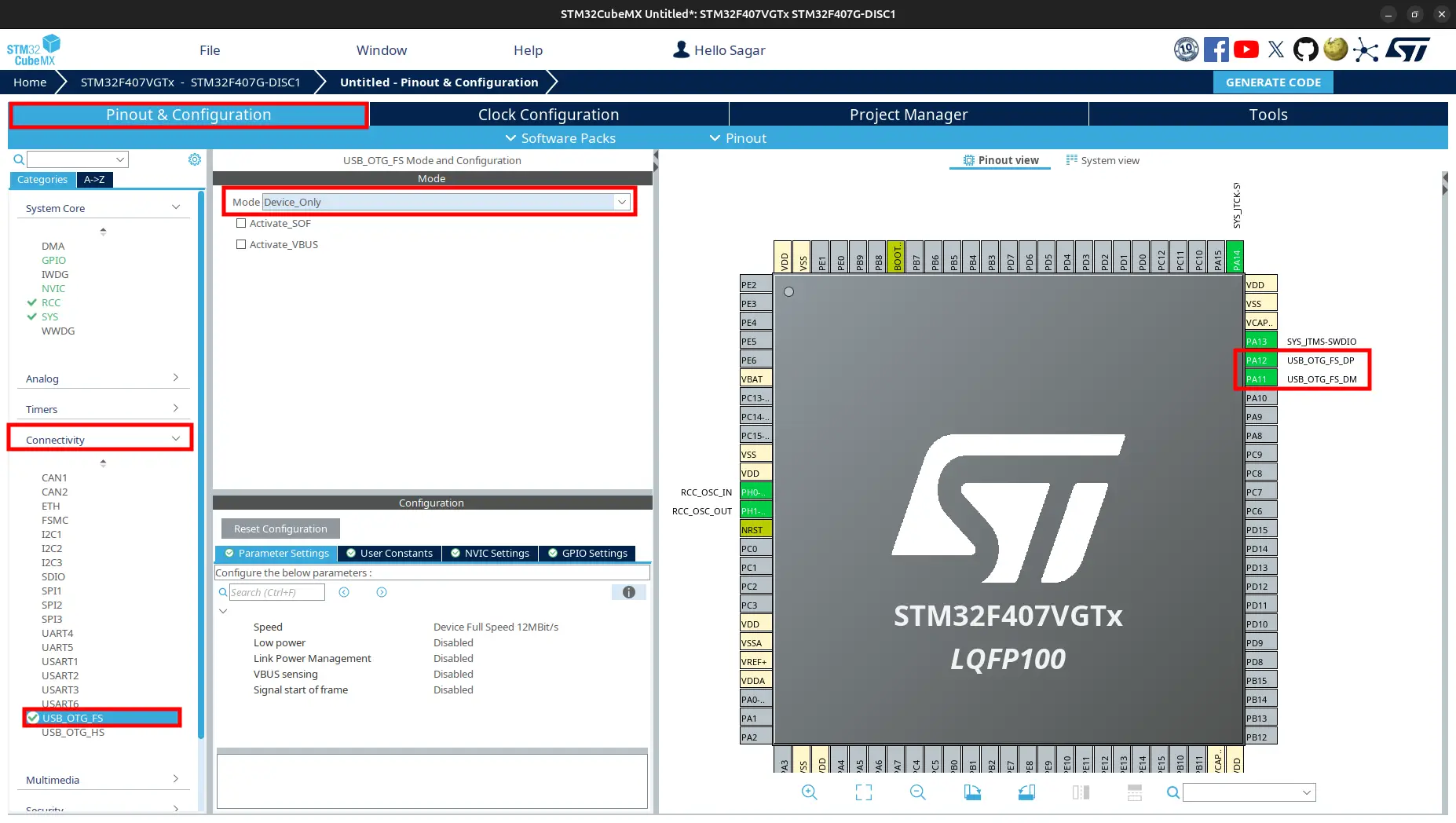
From
Categories, selectMiddleware and Software Packs. FindUSB_DEVICE. ChangeClass for FS IPtoCommunication Device Class (Virtual Port Com.
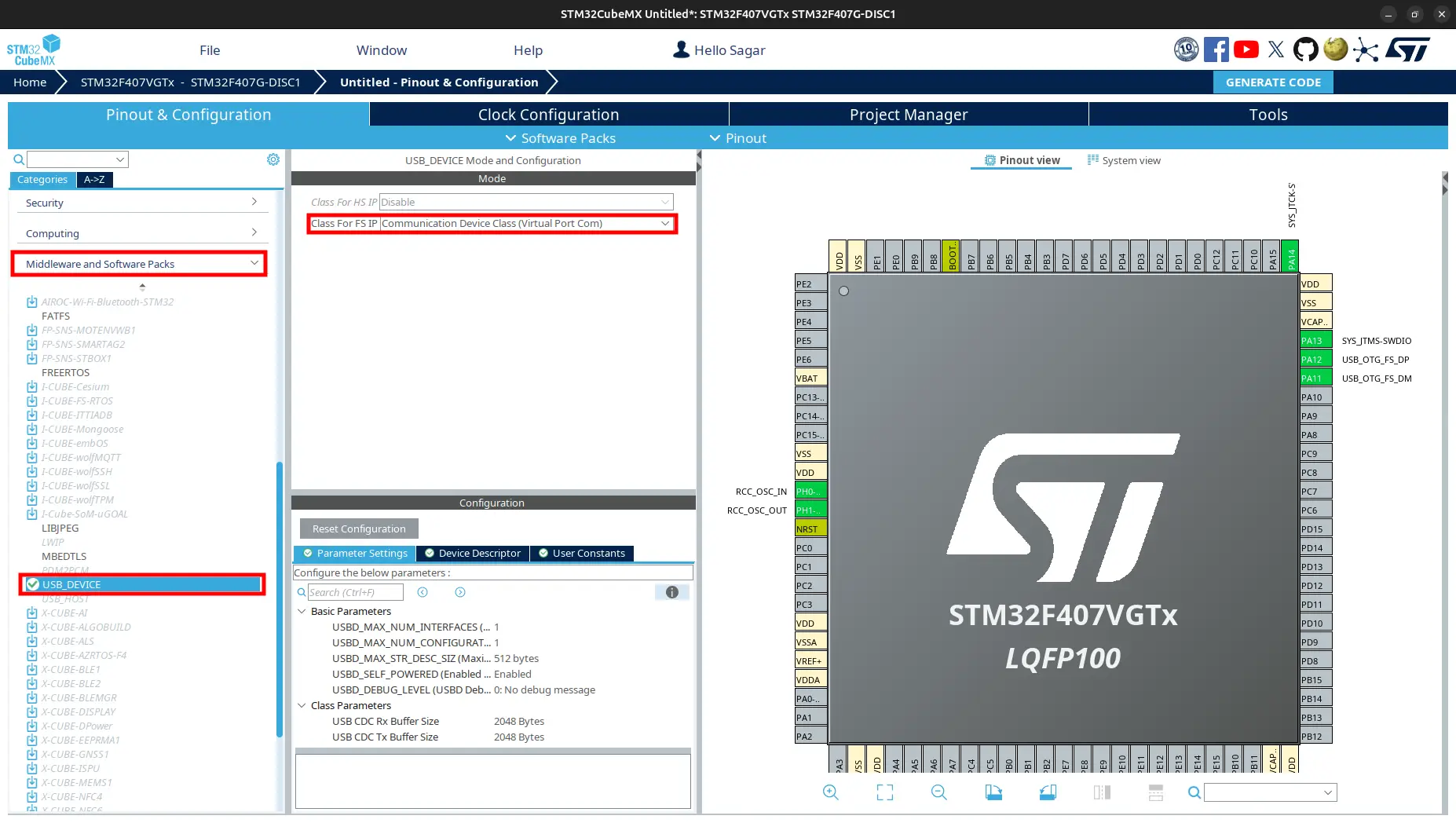
Generate code and open the project.
USB Device Middleware is added to the project. The middleware provides the USB CDC class implementation, configured to use the USB OTG FS peripheral in device mode and to emulate a virtual COM port over USB.
3. Code to Transmit Data using USB CDC
Open project folder and navigate to
Core > Src > main.c.Add header
usb_cdc_if.h./* USER CODE BEGIN INCLUDE */ #include "usbd_cdc_if.h" /* USER CODE END INCLUDE */
Add the following code to the
mainfunction to transmit “Hello World” over USB./* USER CODE BEGIN 2 */ char msg[] = "Hello World\n"; /* USER CODE END 2 */ /* Infinite loop */ /* USER CODE BEGIN WHILE */ while (1) { CDC_Transmit_FS((uint8_t*)msg, sizeof(msg)); HAL_Delay(100); /* USER CODE END WHILE */ /* USER CODE BEGIN 3 */ } /* USER CODE END 3 */
Build and flash.
4. Hardware Setup and Connection
Connect your microcontroller to your PC using USB cable. For simplicity, open Serial Monitor in Arduino IDE. You can see printing “Hello World” on the Serial Monitor continuosly.
You can also use your terminal to see the message from the microcontroller.
Note
This debian package brltty creates issue on finding USB port address, especially for CPxxxx USB driver. So, remove brltty.
sudo apt autoremove brltty
Open terminal. Check the USB Port of the microcontroller. Type command:
ls /dev/ttyACM0 # hit tab after `ACM`.
STM32 microcontroller USB ports are commonly have port address ACM0, ACM1, ACM2 rather USB0, USB1, USB2.
Print serial data on terminal. For USB port ACM0:
cat /dev/ttyACM0
You can see “Hello World” printing continuosly on the terminal.
Warning
Using cat command to read serial data may not print data properlly if the boudrate is other than 115200.
Now you learn to send data over USB using printf in next tutorial.
Warning
Many bluepills found in Nepal have STM32F103C6T6 microcontroller and have only 32KB flash memory. Using USB can overflow the flash memory.
References
References are from STM32 HAL Driver documentation.
-
uint8_t CDC_Transmit_FS(uint8_t *Buf, uint16_t Len)
Transmits data over the USB IN endpoint via the CDC interface.
- Parameters:
Buf – Buffer of data to be sent.
Len – Number of data bytes to be sent.
- Returns:
USBD_OKif all operations succeed, otherwiseUSBD_FAILorUSBD_BUSY.- Note:
This function handles data transmission via the USB CDC interface.